Hubble detecta un intruso astronómico en una galaxia lejana
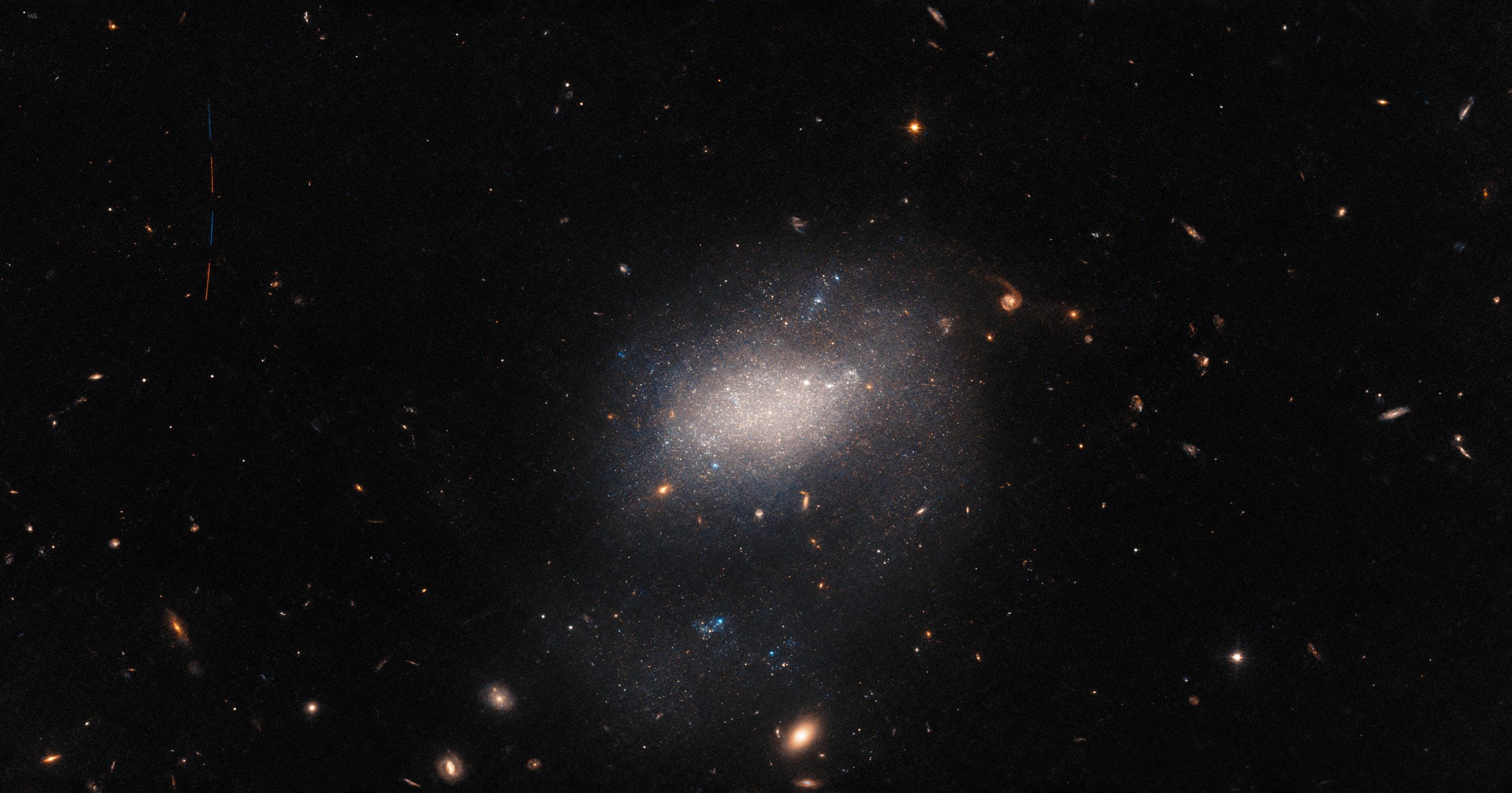

Esta imagen del telescopio espacial Hubble incluye varios objetos astronómicos. Dispersas en la imagen hay galaxias de fondo que van desde espirales imponentes hasta elípticas difusas. También están presentes estrellas brillantes en primer plano mucho más cerca de la Tierra, rodeadas de picos de difracción. En el centro del cuadro, el tenue contorno de la diminuta galaxia UGC 7983 se puede ver como una nube de luz borrosa. Pero escondido dentro de esta imagen hay un intruso cósmico inesperado. Crédito: ESA/Hubble y NASA, R. Tully
Una gran cantidad de objetos astronómicos se agrupan en esta imagen del[{» attribute=»»>Hubble Space Telescope. Background galaxies ranging from stately spirals to fuzzy ellipticals are strewn across the image, and bright foreground stars much closer to home are also present, surrounded by diffraction spikes. In the center of the image, the vague shape of the small galaxy UGC 7983 appears as a hazy cloud of light. UGC 7983 is around 30 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo, and is a dwarf irregular galaxy — a type thought to be similar to the very earliest galaxies in the Universe.
This image also conceals an astronomical interloper. A minor asteroid, only a handful of kilometers across, can be seen streaking across the upper left-hand side of this image. The trail of the asteroid is visible as four streaks of light separated by small gaps. These streaks of light represent the four separate exposures that were combined to create this image, the small gaps between each observation being necessary to change the filters inside NASA/ESA Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS).
Capturing an asteroid was a fortunate side effect of a larger effort to observe every known galaxy close to the Milky Way. When this project was first proposed, roughly 75% of all the Milky Way’s near galactic neighbors had been imaged by Hubble. A group of astronomers proposed using the gaps between longer Hubble observations to capture images of the remaining 25%. The project was an elegantly efficient way to fill out some gaps not only in Hubble’s observing schedule, but also in our knowledge of nearby galaxies.