Telescopio espacial Hubble explora una tarántula turbulenta


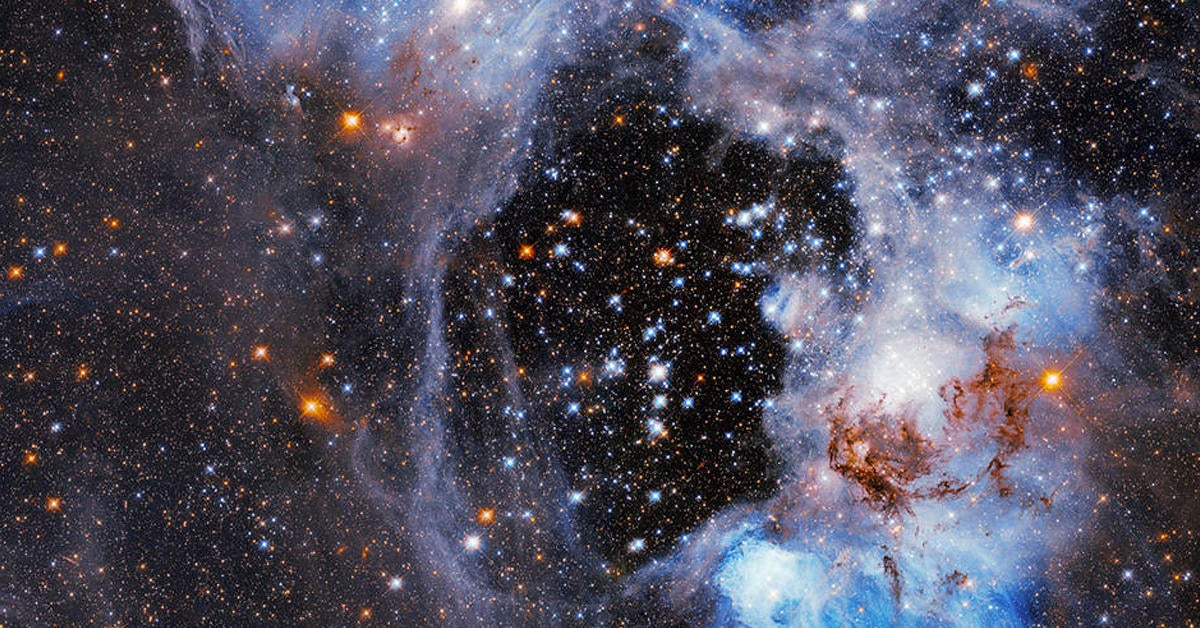
Instantánea del Telescopio Espacial Hubble de la Nebulosa de la Tarántula (también conocida como 30 Doradus). Crédito: ESA/Hubble y NASA, C. Murray, E. Sabbi, Gracias: Y.-H. Chu
Una instantánea de la Tarántula nebulosa (también conocido como 30 Doradus) es el último[{» attribute=»»>Hubble Space Telescope Picture of the Week. The Tarantula Nebula is a large star-forming region of ionized hydrogen gas located approximately 161,000 light years from Earth in the Large Magellanic Cloud, and its turbulent clouds of gas and dust can be seen swirling between the region’s bright, newly-formed stars.
The Tarantula Nebula is a familiar site for Hubble. It is the brightest star-forming region in our galactic neighborhood and home to the hottest, most massive stars known. This makes it a perfect natural laboratory in which to test out theories of star formation and evolution, and a rich variety of Hubble images of this region have been released to the public in recent years. The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope also recently delved into this region, revealing thousands of never-before-seen young stars.

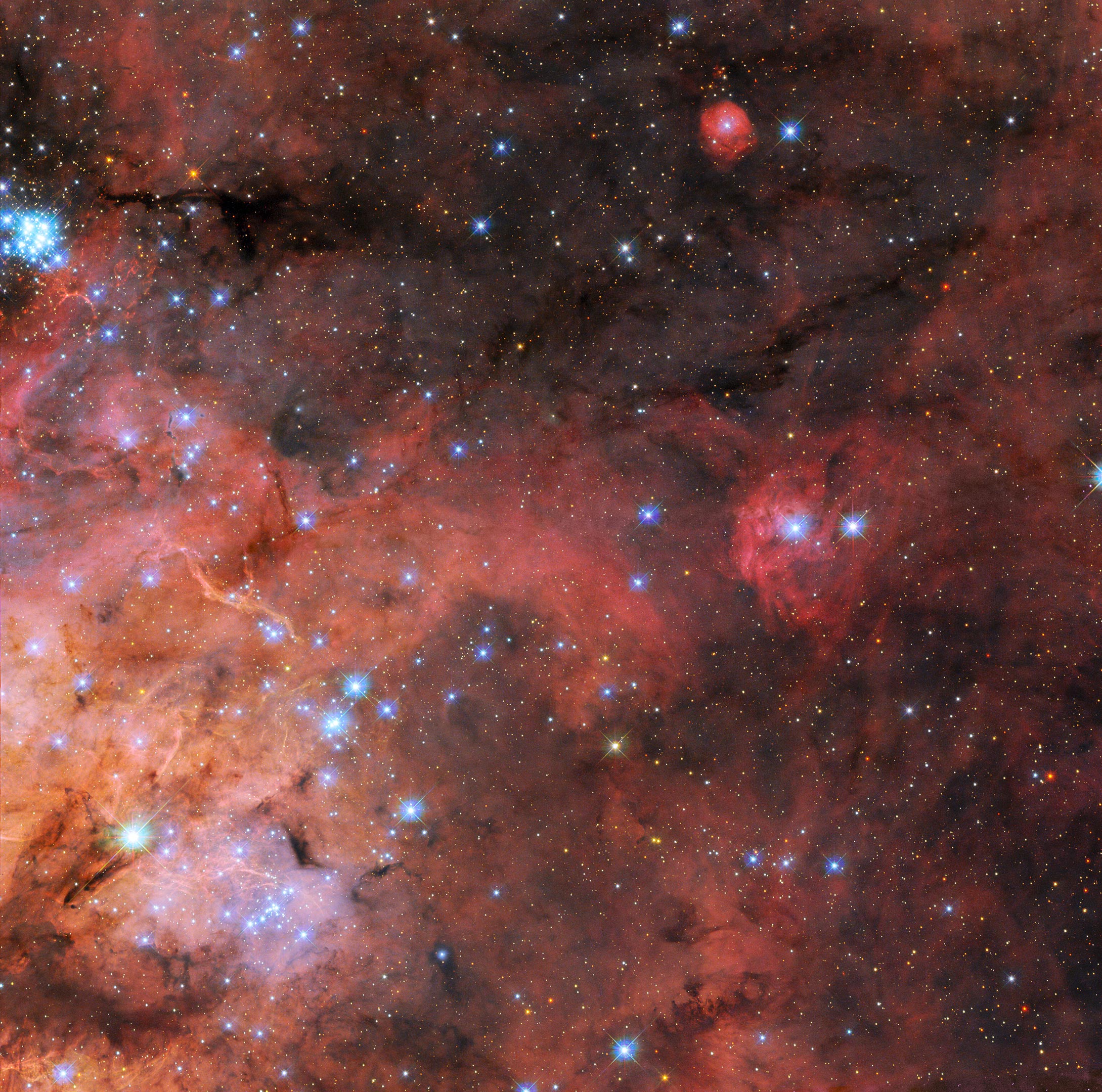
In this mosaic image stretching 340 light-years across, Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) displays the Tarantula Nebula star-forming region in a new light, including tens of thousands of never-before-seen young stars that were previously shrouded in cosmic dust. The most active region appears to sparkle with massive young stars, appearing pale blue. Scattered among them are still-embedded stars, appearing red, yet to emerge from the dusty cocoon of the nebula. NIRCam is able to detect these dust-enshrouded stars thanks to its unprecedented resolution at near-infrared wavelengths. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Webb ERO Production Team
This new image combines data from two different observing proposals. The first was designed to explore the properties of the dust grains that exist in the void between stars and which make up the dark clouds winding through this image. This proposal, which astronomers named Scylla, complements another Hubble observing proposal called Ulysses and is revealing how interstellar dust interacts with starlight in a variety of environments. This image also incorporates data from an observing program studying star formation in conditions similar to the early Universe, as well as cataloging the stars of the Tarantula Nebula for future science with Webb.